WI-FI networks are convenient links users employ to connect to the internet if they do not like dealing with cables. For all the advantages associated with a wireless setup, some problems often threaten to reduce or disrupt its usability.
The WI-FI strength, in theory, is somehow dependent on the space or distance between the connecting device and the router. A good number of users have complained of issues affecting the range of their WI-FI. The problems seem to manifest after an upgrade to Windows 10 from an older version of the operating system.
- If you recently installed Windows 10 on your device, then you probably want to do several things that require internet connectivity. Therefore, setbacks affecting the range of the WI-FI network available to you cannot have come at a worse moment.
- If you have been running Windows 10 on your system without experiencing problems with Wi-Fi networks until now, then you might suffer a similar sense of frustration due to connectivity issues that decided to appear only recently.
In this guide, we will scrutinize the problem and show you how to fix low Wi-Fi signal strength on Windows 10 regardless of how much time has gone by since you started using Windows 10 on your device.
Pro Tip: It is possible to fix many PC issues by using the PC Repair tool. PC Repair is easy to use and reliable Windows optimization software developed to fix hundreds of system issues.
Special offer. About Outbyte, uninstall instructions, EULA, Privacy Policy.
Therefore, we will provide solutions for users who came here to find out how to fix weak WIFI signal after Windows 10 update and fixes for those who began to experience the problem long after the installation of the latest version of Windows.
How to fix Wi-Fi range issues on Windows 10?
We arranged the fixes below in term of their relative usefulness to users. We recommend that you begin with the first procedure on the list. If it fails to give you the effect you desire, then you can continue with other fixes and work your way down until you arrive at what works for you.
- Update your network adapters:
Drivers control the interactions between hardware devices and the software running on them. The driver for a device on Windows allows communication between the hardware component involved and the operating system.
If you are struggling with Wi-Fi range issues, then you need to check the state of your network adapters as they control the interactions that are of importance to us in this case. Most times, the problems involving drivers have something to do with their age or the corruption of their software.
- Generally, you can fix problems with drivers by simply updating the drivers to their latest versions. The operations involved are far from straightforward, though. The first part of the job requires you to identify the drivers involved, and this is no easy task considering the number of drivers available on your PC.
If you correctly manage to identify the drivers that you need to update, then you will come to realize that the next stage of the procedure is even more difficult. You will have to find the updated versions of the drivers that are suitable for your system.
If you are lucky, you might find them after going through a few pages of Google search results. If things end up being different for you, then you might spend the whole day searching for something you might not even find. There are also significant risks associated with the operations involved.
For example, if you download the needed files from unsafe sources, then you might end up infecting your system with a virus or malware, and if such an event occurs, then you will struggle with even worse problems than the one you are facing currently. We could go on and on to describe other issues, but we need not do this if you can avoid the complications and risks.
- We implore you to download and run Auslogics Driver Updater to employ the automatic method of updating drivers, which is the safest, fastest, and the most efficient means of getting the work done. The recommended program will help you execute all the operations you would have had to carry out manually had you decided to do things yourself.

- Roll back drivers:
If your Wi-Fi range problems persist even after you updated your network adapter drivers to the latest versions recommended by the manufacturer of your PC, then a return to the oldest drivers is probably what your computer needs to get past its troubles. Follow these instructions to restore the driver on a system to its default version:
- Press (and hold) the Windows button on your keyboard, then tap the letter X key to bring up a list of programs and options that form the Power User menu. Click on Device Manager to launch the required program
- After the program window comes up on your screen, you will see the list of drivers currently installed on your computer. Go through them and locate Network Adapters, which you must click on to expand its menu. Now you should see the list which consists of drivers that control access to the web
- Click on any driver there. After the Properties window for the selected driver shows up on your screen, you must navigate to the Driver tab. There, you must click on the Roll back driver button you see to return the old driver.
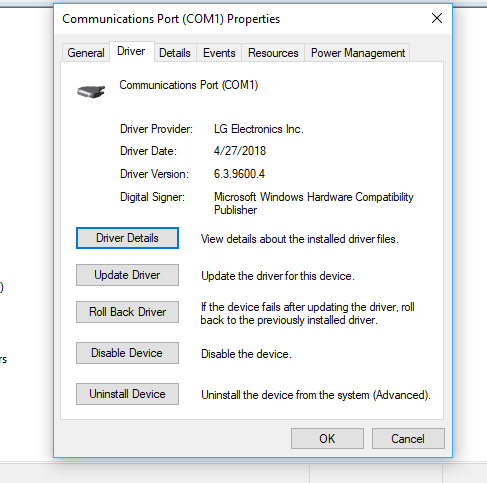

If the button is grayed out or unavailable for selection, then it means your system is still using the old driver, and in that case, an update of the driver is what you need. Check out the first fix.
- Restart your PC to let the new changes become effective. After your computer comes on and Windows settles down, the new drivers will begin their work, and your struggles due to the weak strength Wi-Fi networks might be a thing of the past.
- Set your wireless adapter to work in its maximum performance mode:
To save power on your device, Windows often sets a good number of adapters to work using fewer resources than they are capable of drawing. This setup is useful for the most part, but in times when you are having problems with the range of your wireless network, it makes sense for you to do away with it.
Currently, you need your wireless adapters to work as best as they can. Here are the instructions you need to go through to change your Wi-Fi adapter power settings to Maximum performance:
- Press the Windows button on your keyboard or click on the Windows Start icon that is always visible on your desktop screen. Type in the following keywords into the text field present to do a quick search for them: power options.
From the list of results that appears, click on Power Options (Control Panel)
- After the Power Options menu in a Control Panel program window comes up on your screen, you will see the list of Power Plans that determine the settings for hardware devices and your system in general
- Locate your current Power Plan (the one in use). Click on the Change plan settings link beside it. The Power options window for the selected plan will come up now. From the list of hardware devices or options you see, click on Wireless Adapter Settings
- Change whatever value you find in its Setting to Maximum performance. Once you are done, click on the Apply button, then click on the OK button to save the changes you just made
- Exit the windows you opened. The new configuration should go into effect immediately without you having to restart your PC. Check if your problems involving the range of Wi-Fi networks persist.
Note that instead of modifying the settings for your current plan, you can go with a different plan altogether to achieve the same result. From the plans available under Power options, the High performance mode is the one you have to choose. Nevertheless, your system will use up more power resources if you select this plan as it favors performance in general over saving energy.
- Change some settings for your wireless adapter:
A good number of users confirmed that they had fixed their Wi-Fi range issues and similar problems by simply changing the sensibility value for their wireless network adapter. We are inclined to believe them, and we recommend that you try out the procedure to see for yourself. Follow these instructions:
- Right-click on the Windows Start icon that is always visible on your desktop screen to see a list of programs and options from which you must select Device Manager to launch the application we need
- After the program window comes up, go through the list of device drivers on your PC to locate Network Adapters, which you must click on to expand its menu. Your Wi-Fi adapter will be visible by now. Right-click on it and select Properties from the short menu list that appears
- After the Properties window appears, you must navigate to the Advanced tab. There, under Property, you see a list of options available in the drop-down menu. Select Roaming Sensitivity Level, Roaming Aggressiveness or Roam Tendency, depending on which one you see.
- From the options available in the drop-down menu for Value, select Highest. Perform the same operation on Transmit Power or Transmit Power Level, depending on which one you see. You must also change the value for Antenna diversity to Auto if this option is available for editing
- For Band Preference, we recommend you go with Prefer 802.11a if your wireless network employs frequencies around the 5GHz range. Otherwise, you must choose the Prefer 802.11g/b option if your Wi-Fi network works with frequencies around the 2.4GHz range
- Once you are done making all the necessary alterations, you must save the changes you just made by clicking on the OK button (wherever it is available). You are now free to close the program windows you opened
- Check if the Wi-Fi range issues still plague your PC. If you realize that your problems persist, restart your PC, then verify again after the reboot.
Other things to try
At this point, if you are yet to resolve the problems that affect the range of Wi-Fi network your computer connects to, then this list of additional solutions will do you a whole lot of good. We have included them in fewer details, though, but this takes nothing away from their effectiveness.
- Disable your Bluetooth adapter:
As awkward as it might sound, enough reports have confirmed that some people were able to fix problems causing their wireless adapters to struggle with the strength of Wi-Fi available by merely disabling the adapter for another component (usually their Bluetooth). There is no harm in performing the same or similar action to find out if it works for you too.
- Set your antenna diversity to auxiliary:
Antenna diversity is another option in the properties for a Wi-Fi adapter that might be available for editing. Open the Device Manager program you are used to working on already, then navigate through the necessary menu or options to locate the Antenna diversity option, whose Value you must set to Auxiliary. Things might improve after this change.
- Change the router frequency:
Most manufacturers these days produce routers that employ frequencies around the 5GHz range, but the devices sometimes are not set to do this by default. If your router supports the new technology and your system is okay with it, then you might benefit from a change to it in terms of the signal strength.
- Update your router firmware:
In exceptional cases, the causes of the weak Wi-Fi strength might have nothing to do with your PC—your computer might be blameless entirely. In that case, an update of the firmware for your router is likely the fix you need. The operations involved are far from easy to carry out, though, so you will have to consult your router’s manual or do a lot of research to get the job done correctly.
- Change your wireless setup:
You should consider shaking up things in general. You could replace your wireless antenna with a better one. An alteration of the wireless router channel is not a bad idea. You should consider purchasing a Wi-Fi extender or even replacing your router with a new modern device.
We have come to the end of this guide, and we are glad to have helped you resolve the issues affecting the range or strength of Wi-Fi networks on your Windows 10 computer.